Historical Background of NCRS
The desire by Nigeria to establish its own comprehensive Remote Sensing Centre dates back to 1976, when the Government first made its intentions known during an Inter-Governmental meeting held in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Prior to this pronouncement, several studies undertaken on-behalf of the Government have indicated the need for such a centre to be centrally located. One of such studies was carried out by the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO).
Thus, in 1998, following a decision by the National Council of Ministers, approval was given for a National Centre for Remote Sensing to be established, with its Permanent Headquarters in Jos, and a Satellite Ground Receiving Station at Kerang, near Panyam, Plateau State (site of the defunct Aerostat Balloon project Ref. CM (88) 63,8th Meeting conclusion 5 and CM (88) 175 Meeting of National Council of Ministers.
In 1992, decree 33 established the National Agency for Science and Engineering Infrastructure (NASENI) as a replacement for the Federal Ministry of Science and Technology which became defunct the previous year. NASENI was charged with the responsibility to establish the National Centre for Remote Sensing, amongset other mandates.
Thus, the National Centre for Remote Sensing which formally took off in October 1995 now operates under the aegis of the National Space Research and Development Agency (NASRDA).
Mandates of NCRS
The National Centre for Remote Sensing is charged with the following mandates:
- To undertake pure and applied research, development and to operate Ground Receiving Station capable of receiving data from various satellite systems.
- To undertake action-oriented research and development with the application of RS/GIS technologies.
- To undertake promotional activities such as Conferences, seminars, Workshops, production of Newsletters etc.on the practical applications of Remote Sensing.
- Conduct training programmes for the benefit of resource planners, managers, decision-makers, researchers and the general public.
- To promote and sponsor local development of inventory of natural resources (e.g. solid minerals, petroleum, forestry etc.) and provide data for environmental monitoring and management.
- To encourage and assist public/private sector users to establish in-house Remote Sensing and GIS outfits, and render Consultancy and Extension Services to such outfitsand other organizations.
- To develop joint programmes with any public or private organization whose objectives are in line with national interests for economic development, especially in the field of Remote Sensing, GIS and GPS technologies.
- To generate income through services and sale of products developed by the
Vision
NCRS is committed to being a Centre of excellence in the provision of Geo-informatic services for sustainable Development.
Mission
Advancing knowledge through research and applications of Remote Sensing, GIS and related technologies for the identification, inventory, development and management of natural and human resources.
Core Values
- Professionalism
- Integrity
- Teamwork
- Excellence
Organizational Structure of NCRS
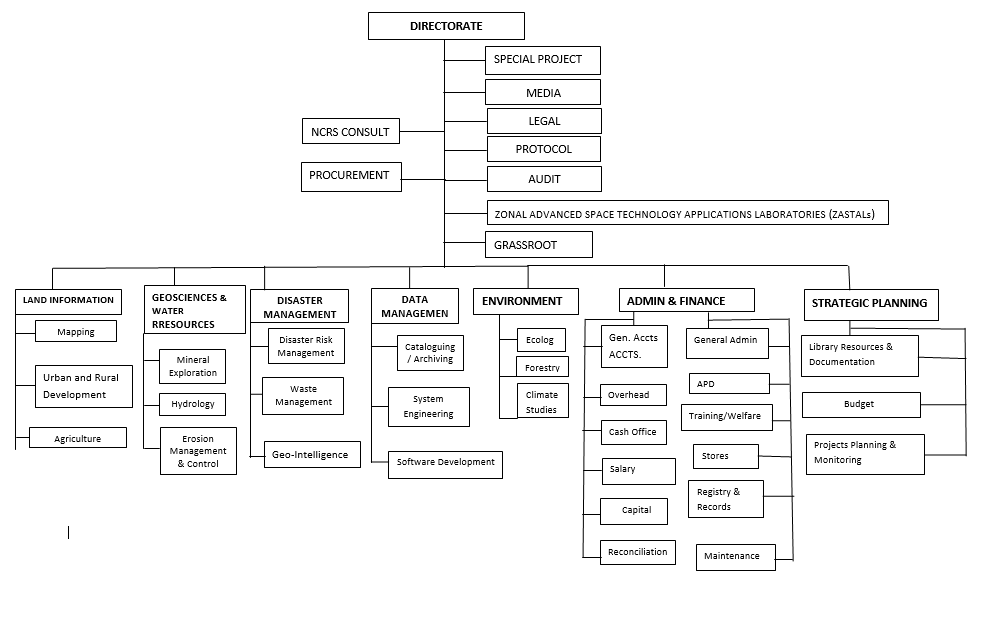
Technology Application Department of NCRS
LAND INFORMATION DEPARTMENT
- Mapping
- Urban & Rural Development
- Agriculture
GEOSCIENCES & WATER RRESOURCES DEPARTMENT
The Department applies GIS and Remote Sensing Technology to research in the following areas
- Mineral Exploration
- Hydrology
- Erosion Management & Control
DISASTER MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT
The Department seeks to use Remote sensing and GIS to investigate Natural and Man-made Disasters
- Disaster Risk Management
- Waste Management
- Geo-Intelligence
DATA MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT
- Satellite Data Archiving/Cataloguing/ICT
- System Engineering
- Software Development
ENVIRONMENT DEPARTMENT
- Ecology
- Forestry
- Climate Studies
DEPARTMENT OF ADMINISTRATION AND FINANCE
The department headed by a Deputy Director is subdivided into two sections, namely; General Administration and Finance Sections. The General Administration Section is further subdivided into units for efficient functioning. There are six Units headed by Chief Administrative/Executive Officer who supervise the activities and staff in each of the units.
Units under Administration Section:
- General Administration Unit: This handles matters related to; Appointment, Promotion, Discipline and Security matters.
- Establishment, Staff Training and Welfare: This takes care of staff Pension matters and gratuity, National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) matter, Staff Training and Welfare, Corps members and IT students.
- Maintenance and Transportation Unit: this Unit handles Office Assets and its maintenance, General cleanliness of premises, etc.
- Registry
- Records
- Store
Units under Finance Section:
- Final Account and Reconciliation: This unit handles preparation of financial statement and preparation of trial balance and reconciliation.
- Central Pay Unit (CPU): This unit makes payment and also keep and maintain cash books and also perform other functions.
- Salary Sections/Personnel: Prepare and pay salary to all staff with the support of IPPIS office. They also keep staff salary matters such as pension, tax, NHF etc.
- Overheads and Capital: This section is in charge of preparation of overhead and capital vouchers.
- Advances and Retirement: This section is in charge of ensuring all staff advances are retired promptly.
- Checking Section: This section is in charge of checking of all payment vouchers to ensure that all supporting documents are included and are inserted into the payment vouchers.
STRATEGIC PLANNING DEPARTMENT
The department, headed by a Deputy Director is subdivided into four sections. These sections all come together in the establishment of a strategy for achieving organizational goals, as well as developing comprehensive plans to integrate and coordinate activities.
Units under planning department:
- Budget: This unit is responsible for the preparation of the Centre’s annual budget and budget projection.
- Library Resources and Documentation: This unit is tasked with the responsibility of housing the Centre’s book collections and journals.
- Projects Planning & Monitoring: This unit is responsible for project planning, project monitoring and evaluation.
- Information Services: The preparation of the Centre’s annual report is performed by this unit.
